Vitamin D is more than just a nutrient; it’s essential for your well-being. Known as the “sunshine vitamin,” it supports healthy bones, boosts immunity, and enhances overall vitality. In this guide, we’ll explore how vitamin D is made, its relationship with sunlight, signs of deficiency, and how to restore it through diet and supplements.
How Vitamin D Is Made
When your skin is exposed to sunlight, it triggers the production of vitamin D. Specifically, ultraviolet B (UVB) rays convert a compound in your skin into vitamin D, which is then processed by your liver and kidneys into its active form. This process is crucial for maintaining optimal levels of the vitamin.
The Sunlight Connection
Sunlight is the best natural source of vitamin D. However, factors like location, skin color, age, sunscreen use, and the time of day can affect your body’s ability to produce it. In regions with less sun or during the colder months, your body may struggle to generate enough vitamin D.
Recognizing Vitamin D Deficiency
Low levels of vitamin D can lead to several health concerns. Common signs include:
- Fatigue and tiredness
- Bone pain or discomfort
- A weak immune system and frequent illness
- Mood changes, including depression
- Hair loss and thinning
- Muscle weakness and difficulty moving
Blood Test for Diagnosis
To accurately determine if you have a vitamin D deficiency, a simple blood test can measure the level of 25-hydroxyvitamin D. Based on the results, your doctor can advise the best course of action to restore balance.
Restoring Vitamin D: Diet & Supplements
Dietary Sources of Vitamin D
There are two effective ways to boost your vitamin D levels: through diet and supplements.
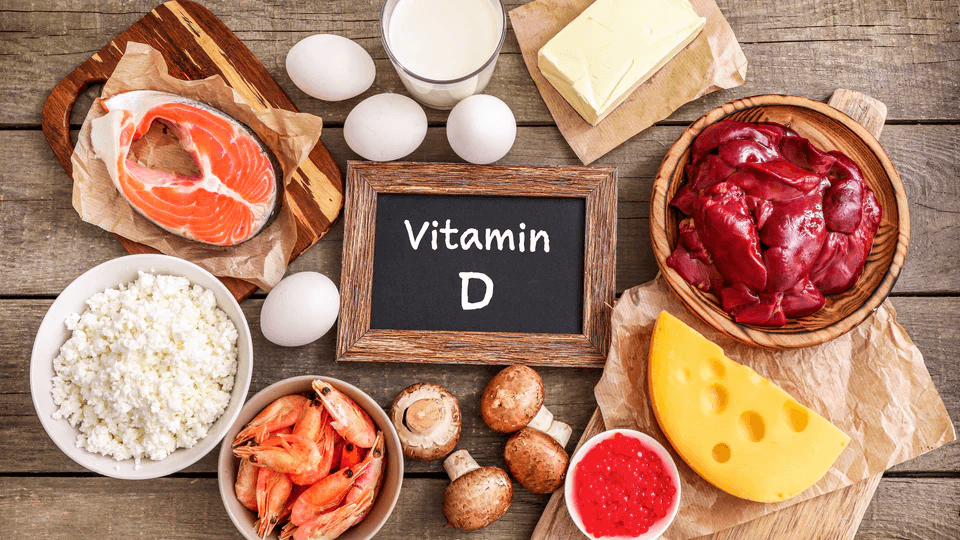
Some foods naturally contain vitamin D. While it can be difficult to get enough from food alone, options include:
- Fatty fish (like salmon and sardines)
- Egg yolks
- Fortified foods (milk, juice, cereals)
- Cheese and liver
Supplements
If diet and sunlight aren’t enough, vitamin D supplements may be recommended. The two main forms are:
- Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol): Plant-based, less effective.
- Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol): Animal-based, more potent and preferred.
Your healthcare provider can help you choose the right form and dosage.
Conclusion
Vitamin D is essential for maintaining a healthy body and mind. While sunlight is the best source, factors like lifestyle and geography can limit your exposure. If you’re concerned about your vitamin D levels or experiencing symptoms, speak to a healthcare professional at OneMedicine Private GP Clinic. We’ll guide you in restoring your vitamin D to keep you feeling your best.
















