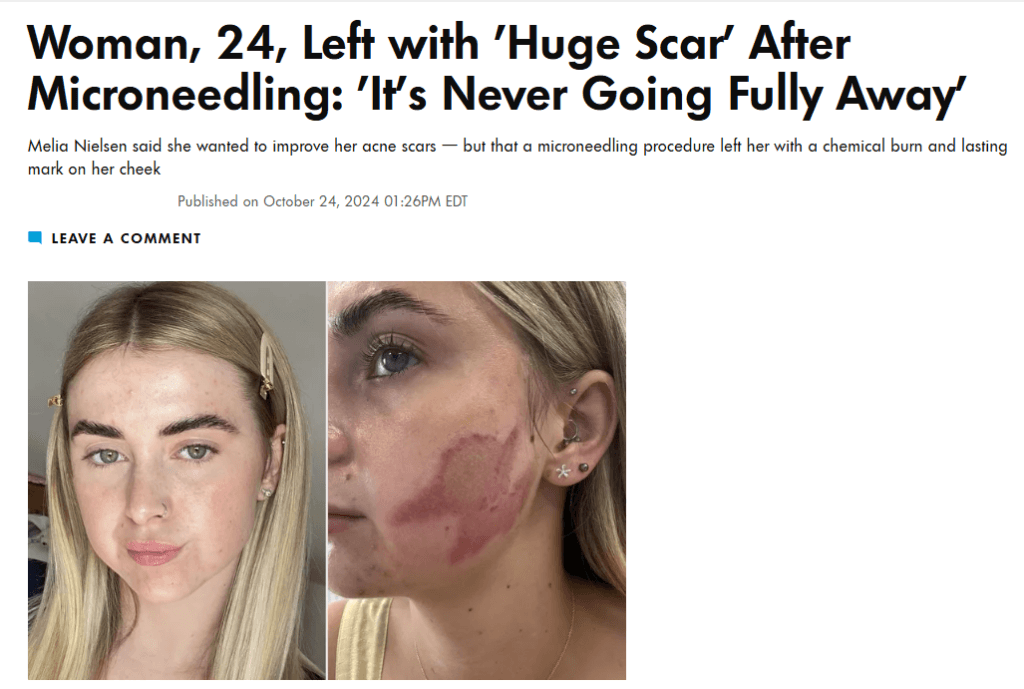
Microneedling is a popular aesthetic treatment in the UK for improving skin texture, acne scarring, fine lines, and overall skin quality. It works by creating controlled micro-injuries in the skin to stimulate collagen production and natural healing processes. When performed correctly, microneedling is generally safe and effective.
However, microneedling is not a cosmetic facial. It is a procedure that intentionally breaks the skin barrier, and complications can occur. Evidence from clinical practice shows that the risk of complications is significantly influenced by the practitioner’s level of medical training, anatomical knowledge, and ability to assess suitability.
Understanding why medical training matters is essential when considering microneedling.
- Common Side Effects After Microneedling
- Infection Risk and the Importance of Medical Asepsis
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation and Skin Type Assessment
- Scarring Risk and Anatomical Knowledge
- Prolonged Redness and Inflammatory Skin Conditions
- Acne Flare-Ups and Treating the Right Skin at the Right Time
- Allergic and Granulomatous Reactions
- Nerve Irritation and Depth Control
- Managing Expectations Through Medical Consultation
- Increased Risks Outside Medical Settings
- Why Medical-Led Microneedling Is Safer
- Final Thoughts
Common Side Effects After Microneedling
Temporary redness, warmth, swelling, skin tightness, tenderness, and pinpoint bleeding are common and expected after microneedling. These effects reflect the normal inflammatory response required for collagen stimulation and usually resolve within 24 to 72 hours with appropriate aftercare.
Medical practitioners are trained to distinguish between normal healing responses and early signs of complications, allowing prompt intervention if recovery does not progress as expected.
Infection Risk and the Importance of Medical Asepsis
Infection is one of the most serious microneedling risks reported in the UK. The microscopic channels created during treatment allow bacteria and viruses to bypass the skin’s natural defence barrier.
Medical training provides a clear advantage through:
✔ Strict aseptic technique
✔ Use of sterile, single-use needle cartridges
✔ Medical-grade skin preparation
✔ Recognition of early infection signs
Infections may present with worsening redness, pain, swelling, discharge, or delayed healing. Viral reactivation, particularly cold sores, is also recognised. Medical clinicians are trained to identify patients who may require preventative antiviral medication and to initiate timely treatment should infection occur.
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation and Skin Type Assessment
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation is one of the most underestimated risks of microneedling in the UK, particularly in patients with medium to darker skin tones.
Medical practitioners are trained in:
✔ Skin typing and pigment risk assessment
✔ Adjusting needle depth based on skin structure
✔ Reducing inflammatory load during treatment
✔ Pre- and post-procedure skin preparation
Understanding melanocyte behaviour and inflammatory pathways allows medically trained clinicians to minimise pigmentation risk and manage it appropriately should it occur.
Scarring Risk and Anatomical Knowledge
Permanent scarring from microneedling is rare but possible, particularly when needle penetration is excessive or technique is aggressive.
Medical training provides a critical advantage through:
✔ Detailed knowledge of skin anatomy
✔ Understanding dermal thickness variation across the face
✔ Avoidance of high-risk areas
✔ Recognition of patients prone to hypertrophic or keloid scarring
This anatomical knowledge significantly reduces the risk of permanent skin damage.
Prolonged Redness and Inflammatory Skin Conditions
Persistent redness or chronic inflammation following microneedling is more likely in patients with rosacea, sensitive skin, or underlying inflammatory skin disorders.
Medical assessment allows:
✔ Identification of underlying skin conditions
✔ Modification or avoidance of treatment when appropriate
✔ Safe management of prolonged inflammation
This reduces the risk of long-term skin sensitivity and distress.
Acne Flare-Ups and Treating the Right Skin at the Right Time
Microneedling should not be performed over active inflammatory acne. Medical clinicians are trained to differentiate between acne types and inflammatory activity, reducing the risk of bacterial spread, scarring, and post-acne pigmentation.
Appropriate patient selection is one of the strongest safeguards against complications.
Allergic and Granulomatous Reactions
Granulomatous reactions can occur when inappropriate or non-sterile products are introduced into the dermis. Medical-led clinics use injectable-grade, sterile products and understand immunological skin responses, significantly reducing this risk.
Nerve Irritation and Depth Control
Aggressive or deep microneedling can irritate superficial sensory nerves, leading to prolonged tenderness or altered sensation.
Medical training provides:
✔ Precise depth control
✔ Awareness of nerve distribution
✔ Conservative treatment planning in high-risk areas
This minimises neurological complications.
Managing Expectations Through Medical Consultation
Microneedling delivers gradual, cumulative improvement and is not a substitute for surgical or injectable procedures. Medical practitioners are trained to provide realistic counselling, reducing dissatisfaction and psychological distress caused by expectation mismatch.
Increased Risks Outside Medical Settings
A disproportionate number of serious microneedling complications in the UK arise from:
- Home microneedling devices
- Beauty salons without medical oversight
- Inadequate training or poor infection control
These settings lack the clinical assessment, anatomical knowledge, and complication management skills required for safe treatment.
Why Medical-Led Microneedling Is Safer
Medical training allows:
✔ Proper patient selection
✔ Accurate risk assessment
✔ Conservative and individualised treatment
✔ Early recognition of complications
✔ Access to prescription-only treatments if required
These factors collectively reduce complication rates and improve outcomes.
Final Thoughts
Microneedling is a medical skin procedure that relies on controlled injury and healing. While most patients experience only mild and temporary side effects, complications can be prolonged and difficult to reverse when they occur.
Choosing a medically trained practitioner in the UK provides a clear safety advantage through deeper anatomical knowledge, clinical judgement, and the ability to manage complications effectively.
















